Can I Back Flush 4.5 X 20 Iron Filter
In that location is a vast range of dissimilar sediment filters in the market identify, and selecting the right filter for your application can be a real challenge with unforeseen caveats. To decide what sediment filter would exist fit for purpose depends on a number of factors especially the source of water, flow charge per unit required and the application. By and large, it does involve some trial and fault and trialling diverse types of filters and micron sizes and observe which one's work for you. The purpose of this article is to provide some guidelines to select the right sediment filter that will provide satisfactory results.
Sediment Filters should be installed for a number of reasons, and the application, equipment and entire reticulation excursion should be considered. Sediment tin can crusade:
Excessive habiliment within pump, especially impeller components.
Harm to seals, gaskets and diaphragms of pumps, valves and other parts.
Damage to other upstream filtration, especially membrane filtration.
Reduced life bridge of other filters similar carbon cake.
Excessive wear inside plumbing, and can crusade erosion corrosion.
Clog up irrigation sprinkler heads.
Terminology
To start off we demand to offset embrace some terminology, so we can understand some of the features of sediment filters and h2o quality parameters.
Microns: The smaller the micron number, the smaller the particles that can exist filtered out. For point-of-employ applications that include contrary osmosis, we normally recommend a i or 5 micron sediment filter. The smaller micron filters will filter out smaller particles, all the same will clog upward faster causing pressure level drops in the arrangement resulting in decreased flux. One micron is 0.001 mm.
Particle size: Understanding what are the contaminants in your raw h2o and the relative particle sizes are crucial in selecting the right sediment filter.

Turbidity: Turbidity is a mensurate of water clarity how much the fabric suspended in water decreases the passage of light through the h2o. Suspended materials include soil particles (clay, silt, and sand), algae, plankton, microbes, and other substances. These materials are typically in the size range of 0.004 mm (dirt) to i.0 mm (sand). Turbidity tin can affect the colour of the water. Turbidity is by and large measured past using a turbidity meter and measured in NTUs. (Nephelometric Turbidity Units)

If your turbidity is in a higher place 50 NTU you lot should consider using coagulation and/or flocculation to settle out the effectively particles.In colloid chemical science, flocculation refers to the procedure by which fine particulates are caused to dodder together into a floc. The floc may so float to the summit of the liquid (creaming), settle to the bottom of the liquid (sedimentation), or be readily filtered from the liquid. If you have a dam and it takes a long time for the fine material to settle, chances are that there is a significant amount of clay particles in your water. This can cause problems for most filters and hence has to exist be removed by techniques such every bit using a flocculant. It should be noted that flocculants similar alum may crave pH correction too, to prevent a decrease in pH. Organics can contribute to increased turbidity by leaching tannins into the water, and these are more difficult to remove. These tannins are complex organic compounds and are all-time dealt with using ion exchange engineering science specific to organics(tannin filters).
Total Suspended Solids: Full suspended solids are a total quantity measurement of solid cloth per volume of water. This means that TSS is a specific measurement of all suspended solids, organic and inorganic, by mass. Turbidity and TSS are the about visible indicators of water quality. These suspended particles can come from soil erosion, runoff, discharges, stirred lesser sediments or algal blooms. Both organic and inorganic particles contribute to the suspended solid content.
Total Suspended Solids (TSS) are solids in water that can be trapped by a filter. TSS tin include a wide multifariousness of material, such as silt, decomposable institute and animal matter, industrial wastes, and sewage. In commercial aquaculture operations an important component of recirculating water, is to remove suspended solids, typically using a rotarydrum filter.This is usually followed up past a biological filter, to ensure that nitrogen and phosphorous is not returned dorsum into the grow-out ponds.
Total Dissolved Solids: "Dissolved solids" refer to whatsoever minerals, salts, metals, cations or anions dissolved in water. Full dissolved solids (TDS) contain inorganic salts (principally calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, bicarbonates, chlorides, and sulfates) and some small-scale amounts of organic thing that are dissolved in water.
Total Dissolved Solids cannot be trapped past a filter, unless it is membrane technology like reverse osmosis and nanofiltration which can physically remove ions from water by virtue of particle exclusion.
Nominal Filter Rating: The H2o Quality Association (WQA) classifies this filter will filter out at least 85% of the particles of the size it is rated for. In other words, a filter that is rated as a 1 micron nominal can be expected to pick out 85% of the particles that are one micron or larger from the water that passes through it.
Accented Filter Rating: The filter will reject most all of the particles of the given size. The usual expectation is a 3-log rejection–or 99.ix%. Absolute ratings are ordinarily used for the tightest filters and for purposes where efficiency really matters. For example, if a filter maker promises removal of E. coli, more or less 85% efficiency isn't good enough. If you're going to trust your life to the filter, you expect an absolute 3-log or 4-log rating at the very least.
Pleated Sediment Filters: Pleated Sediment Filter Cartridges are most commonly fabricated from pleated reusable polyester fabric. The media has been pleated to provide a very large surface expanse in order to maximise the cartridge dirt holding capacity and extend the fourth dimension between cleaning. Pleated cartridges are particularly useful for low pressure applications such as domestic supplies using header tanks or roof water.
Depth Sediment Filters require the water being filtered to pass through a thick wall of filter cloth and treatment takes place throughout the depth of the sediment filter. Some sediment depth filters, in fact, take what is chosen a "graded density" structure, meaning that the filter gets tighter equally the water passes through the filter wall. Graded sediment density filters remove particles of a variety of sizes. The exterior traps larger particles and smaller particles go trapped towards the inner core.
Sediment Depth filters can be of the wound string blazon or what is called "cook blown." Wound string is probably the nigh common. Depth filters are fabricated of a diversity of materials, including ceramic, cellulose, polypropylene, acrylic fibre, glass fibre, and polyester.
Ceramic sediment filters are simply extremely tight depth filters made of ceramic. They normally have absolute ratings and are tight enough to filter out some microorganisms.
Cartridge style sediment filters generally have a radial flow pattern where water flows through the outer surface towards the inner core.
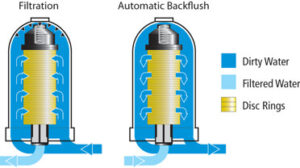
A disc filter is a type of water filter used primarily in irrigation, like to a screen filter, except that the filter cartridge is made of a number ofdiscs stacked on height of each other similar a pile of poker fries. The water passes through the small grooves in betwixt and the impurities are trapped behind. These can be manually cleaned or be automatic to facilitate a cleaning cycle.
An innovative filtration solution for removing sand , silt and other sediment are the centrifugal spin downwardly filters – popular brands areRusco Spin Down Filter and Lakos Twist II Clean. The TwistIIClean allows for effective cleaning performance, featuring an easy ¼-twist meridian handle to create a patented reverse-flushing activity to more than finer remove sand/sediment from the screen surface. Overall, that means reduced maintenance, longer run times, less pressure loss, improve filtering.
A popular blazon of sediment filter used especially for bore , dam and river water filtration is the versatile backwash filter . These backwash filters can exist automated or manual assuasive filtration to as low as 5 microns using Zeolite or activated glass media. It is of import to note that where dirt is present, coagulant or flocculant dosing would be required to ensure particles are large plenty in order to be captured by the media bed. Manual or automated backwash ensures that the media bed is expanded or fluidised resulting in the removal of sediment in the backwash.

Point-of-employ (POU) Filtration: This unremarkably encompasses counter pinnacle and undersink filtration for instance in the kitchen.
Point-of-entry (POE) Filtration: Water is filtered earlier entering the business firm and is reticulated to all house agree fixtures that require water.

The Water Source.
The h2o source plays an of import role in selecting the blazon of sediment filter called for a specific application. As a general rule it is recommended to conduct a water analysis, especially if the h2o supply is from a diameter (well), dam, river, creek or rain water tank. There are water test kits available that allows any person to conduct their own testing for selected h2o quality parameters, including microbiological testing.
Municipal Water: For municipal h2o, the choice is much easier as this water typically contains low levels of sediment and suspended solids. The sediment filter oftentimes serves the purpose of protecting the more than expensive carbon block filter which usually has a 5 micron rating. A one to 5 micron depth filter is normally chosen for this application, peculiarly if a reverse osmosis is one of the filtration stages.
All private water supplies intended every bit drinkable h2o should include a disinfection step like UV or ozone disinfection.
Rain Water: Pelting water quality can be variable and contains a wide variety of contaminants including organic matter like leaves, tannins, and faeces from animals, dust and other pollutants. A 10 to twenty micron pleated filter is normally used prior to the carbon filter. The carbon filter should include a supplementary media like KDF or nano argent to inhibit biofilm germination within the carbon bed. For signal of entry (whole business firm) applications a jumbo filter housing with suitable cartridge (4.5" x twenty") is highly recommended. The selection of the sediment filter may exist a bit trial and error, and if the filter clogs up too quickly, a larger micron sizing may accept to be selected. More about pelting h2o filtration.
Bore Water: The selection of sediment filters should but be considered once a water test has been conducted. Diameter water may require a number of treatments that will touch on the choice of sediment filter, some examples below:
Iron and Manganese: Depending on levels will crave a catalytic oxidation treatment to filter out the resulting precipitants in a downstream backwash sand filter. Sediment cartridge filtration not recommended.
Hard Water: Will crave an ion exchange water softener or nanofiltration stride to remove the hardness salts from the h2o. Sediment filter will not remove whatsoever hardness equally the magnesium and calcium salts are in solution. Magnetic, electrical conditioners or whatever other useless devices are not recommended.
pH of water: If h2o is acidic or alkaline pH correction will be required. Cartridge filtration not recommended for whole house filter applications.
Heavy metals: Will crave a backwash filter with suitable media to remove the contaminant, like Metsorb HMRG.
Generally, aftermath sand filters are recommended for bore water applications. Cartridge mode sediment filters tin be considered for secondary betoken-of-utilize treatments.
Surface Waters: The h2o quality parameters of surface waters can be variable and heavily contaminated from run-off. A broad variety of contaminants like organic affair, pesticides and loftier silt content may require a host of filtration stages. Loftier turbidity water will require description, flocculation and backwash sand filtration to allow for farther treatment steps. A cartridge manner filter similar a pleated washable filter can be considered in the final stages, for example prior to disinfection. For UV – disinfection 5 micron filtration is required in club to optimise the penetration of UV-light.
Cartridge style sediment depth filters can be considered for secondary betoken-of-employ treatments.
Flow Charge per unit Required
In general, menstruum rates for sediment filters are higher than for equally sized carbon or media filters. The tighter the filter, the slower the recommended menses rate and the higher the pressure driblet. As a general guideline the tabular array below suggests flow rates (litres per minute) vs microns for a pleated 9.75″ X ii.5″ filter cartridge:
| Microns | Flow Rate (lpm) |
| 1 Micron Absolute | 11 |
| ii Micron Nominal | xv |
| 5 Micron Nominal | 26 |
| twenty Micron Nominal | 30 |
| 50 Micron Nominal | 38 |
Tabled below, are suggested maximum flow rates in lpm for the four nearly common cartridge sizes. These are indicative menstruation rates and may vary depending on the manufacturer. These are washable and reusable (5 micron and larger) pleated cartridges.
| Micron Rating | two.5 X 9.75 | 2.five Ten 20 | 4.5 10 10 | 4.v X xx |
| 1 Absolute | 11 | 23 | thirty | 45 |
| 0.35 Nominal | fifteen | 30 | 34 | 49 |
| ane Nominal | 15 | 30 | 38 | 57 |
| 5 Nominal | 26 | 53 | 57 | 95 |
| twenty Nominal | 30 | 61 | 57 | 95 |
| 50 Nominal | 38 | 76 | 57 | 95 |
Pressure Drop
Most manufacturers of cartridge filters can provide graphs that show the human relationship of menstruation charge per unit vs. pressure drop, and that needs to be taken into consideration. The pressure drop does progressively increase, as the cartridge takes upwards more clay. The pressure drib across a cartridge filter is used to determine the status and effectiveness of the cartridge. A high pressure drop beyond a cartridge filter, over the maximum recommended pressure drop, indicates that the cartridge needs attention. A 70 kPa pressure drop is normally an indicator that the cartridge needs to be replaced. No pressure driblet at all indicates that the filter is either breached or that the seals are non working, and once again needs attention. In most cases the attending needed is cartridge replacement. With some of the pleated filter cartridges, a cleaning tin can restore an adequate pressure drop.
Pressure gauges are recommended upstream and downstream of the sediment filter, as that is a useful diagnostic tool to evaluate the status of the cartridge.
In commercial applications where backwash filters or other automatic self cleaning filters are used, the backwash tin can be initiated past differential pressure level. This means as the filter progressively builds up with sediment, the overall supply pressure drops to a point where an automatic aftermath and rinse bicycle is initiated.
Determination -Sediment Filter Selection:
Cartridge sediment filters are effective in the removal of moderate amounts of particles from liquids in the size range of fifty to 0.035 microns. When filtering large amounts of solids at loftier flowrates, other treatment methods such as self-cleaning multimedia filters may be required every bit pre-filters, followed past cartridge sediment filtration, if needed.
The selection of sediment filters depends on a number of factors including water quality, flow rate required and application. In many cases, it does involve some trial and error, and frequent filter replacement may require an increase in micron rating to reduce the pressure drop across the filtration stages. For domestic point-of-use reverse osmosis systems a one to 5 micron depth sediment filter is recommended. For whole house point-of-entry applications, pleated sediment filters can be used, depending on the turbidity and quality of the water.
For high flow applications, every bit a general rule it is recommended that aftermath media filters should exist used. Sand separators could also be an choice. The decision may as well exist an economical one where the higher cost of backwash filtration equipment has to be weighed up against the cheaper cartridge –style filtration. Aftermath sediment filtration, especially when automated offer the advantages of minimising operator intervention. There are some very efficient media available that can filter to 1 micron including activated glass media .

Search Terms:
Cartridge Filters, Sediment Filters, Depth Filters, Multi Media Filters, Pleated Filters, Sediment Removal, Iron Removal Filters, pH correction, Self-Cleaning Filters, Aftermath Filers, Sand Filters, Pressure Gauges, Heavy Metals removal, Bore water handling, H2o Softener, Rain H2o Treatment ,River Water Handling, activated glass media
Can I Back Flush 4.5 X 20 Iron Filter,
Source: https://pacificwater.com.au/selecting-sediment-filters-domestic-rural-water-filtration/
Posted by: vitelafaidn1989.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Can I Back Flush 4.5 X 20 Iron Filter"
Post a Comment